Army Branches - Explore Officer Career Fields
When exploring Army branches, cadets consider factors like their long-term goals and career interests, as well as the culture and lifestyle of each branch.
Army Branches - Explore Officer Career Fields
When exploring Army branches, cadets consider factors like their long-term goals and career interests, as well as the culture and lifestyle of each branch.
Breadcrumb
Military Education
Branches by Category
The U.S. Army branches can be categorized into Operations, Operations Support, Force Sustainment, and Information Dominance, each focusing on different aspects of military operations.
- Operations: The operations process involves planning, preparing, executing, and assessing a mission.
- Operations support: Support operations ensure that military forces are ready and effective.
- Force Sustainment: Sustainment operations provide the logistics, maintenance, and support needed to keep military forces ready and effective.
- Information Dominance: Information dominance may be defined as superiority in the generation, manipulation, and use of information sufficient to afford its possessors military dominance.
Operations
The operations process includes planning, preparing, executing, and assessing a mission.
This category includes soldiers and units that are directly involved in combat or combat-like missions. It covers things like infantry, armor (tanks), artillery, aviation (helicopters), and special operations forces. These are the people and teams that are on the front lines or closely support those who are.

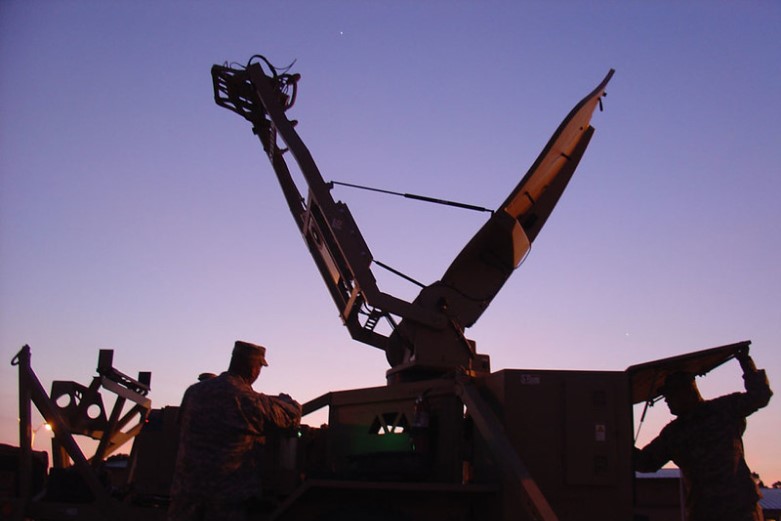
Air Defense Artillery
The Air Defense Artillery (ADA) branch specializes in anti-aircraft weaponry and maintains air space superiority to protect troops against aerial and missile attacks. They provide threat detection and early warnings from airspace.

Armor
Armor officers are responsible for tanks, other mounted vehicles, and soldiers to conduct reconnaissance, surveillance, and target acquisition operations on the battlefield. They are the eyes and ears of the commander.

Aviation
The Aviation branch coordinates aviation operations from maintenance to control tower operations to tactical flight operations. Army aviators provide quick-strike and long-range target engagement and transport troops and supplies.

Chemical Corps
The Chemical Corps uses the latest defense technology to protect the force from chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) weapons and weapons of mass destruction.

Engineer Corps
Army Engineers lead the way by combining technical expertise with tactical skill. Whether building bridges under fire, clearing obstacles in combat zones, or constructing airfields and critical infrastructure, Engineer Officers enable mobility for friendly forces and deny it to the enemy. They design, build, and maintain roads, bases, and airfields, manage natural resources, and oversee large-scale civil works projects—all while supporting combat operations with engineering solutions that ensure mission success.

Field Artillery
Field Artillery provides cannon, rocket, and missile fire support in an operational environment, earning it the title "King of Battle."

Infantry
The Infantry Branch is the main land combat force. Infantry officers are tactical masters who plan and execute worldwide Army operations during war and peacetime.

Military Police
The Army depends on military police to maintain order and discipline. MPs serve as the Army's law enforcement and security officers and handle crimes committed on Army installations.
Operations Support
Support operations include tasks like ensuring that the Army has the equipment needed for training, exercises, combat, and other scenarios.
These are the professionals who help the frontline forces do their job effectively. This includes intelligence experts who gather and analyze information about the enemy, and communications specialists who ensure secure and reliable communication. It also includes people responsible for training and developing Army forces—basically those who make sure the Army is well-prepared and properly equipped for its missions.

Military Intelligence
Military Intelligence officers provide essential information that can often save the lives of Soldiers fighting on the front lines. They lead intelligence soldiers, assess risks, and act to neutralize intelligence threats.

Signal Corps
Signal Corps is responsible operating and maintaining the Army's data systems and resources. Their experts ensure seamless communication end-to-end, including everything from phones and computers to routers and satellite relays.
Force Sustainment
Sustainment is a warfighting function that provides personnel, logistics, and other support to maintain and prolong operations. Sustainment operations are used to build and maintain combat power.
This group keeps the Army running. It includes logistics (like supply and transport), human resources, and financial management—everything that ensures soldiers are fed, equipped, paid, and supported. These roles aren't necessarily on the front lines, but the Army couldn’t function without them. They often are embedded within the Operations Units though.
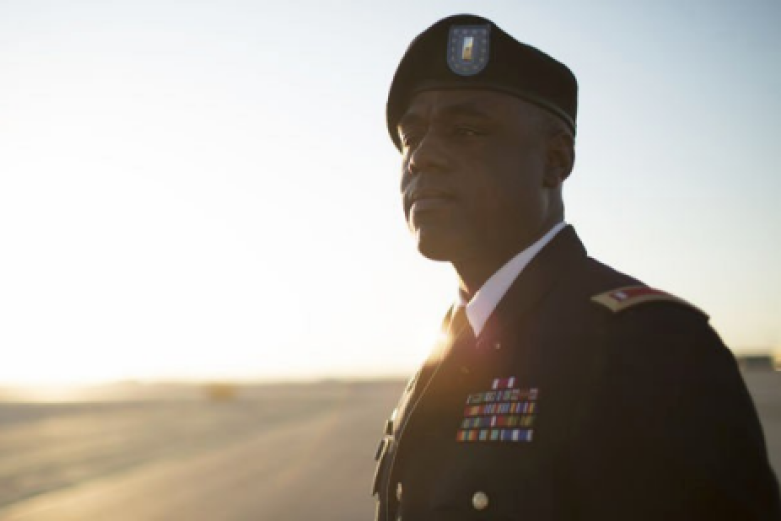

Adjutant General
The Adjutant General Corps is responsible for personnel management. AG officers provide personnel support that affects soldiers' overall welfare and well-being while assisting commanders by keeping soldiers combat-ready.

Finance
Financial managers are responsible for purchasing services and supplies to sustain missions, Army pay, commercial vendor support, auditing, accounting, financial management information systems, and banking.
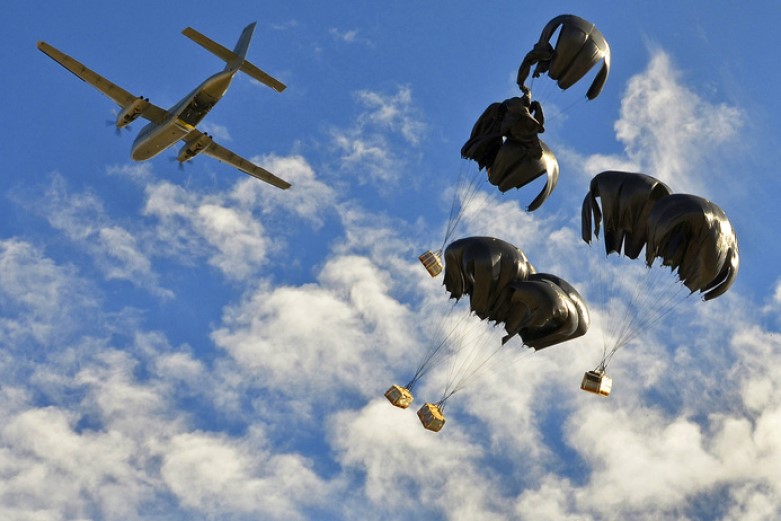

Logistics
The U.S. Army Logistics Branch is responsible for planning, coordinating, and executing the sustainment of Army forces, ensuring that they are equipped, supplied, and maintained for operations both in peacetime and during wartime. It encompasses various functions like supply, maintenance, transportation, and field services, all working together to provide the necessary support for mission accomplishment.
Medical Services
The Medical Service Corps officers plan, direct, manage, administer and participate in the functioning of health care facilities and organizations. They advise commanders at all levels on aspects of health care facilities and delivery.
Information Dominance
Information Dominance is a crucial element for achieving operational advantage. It refers to the degree of information superiority that allows a commander to effectively use information systems and capabilities to gain a tactical edge while simultaneously denying those capabilities to the adversary. Information dominance is not about simply having more data than the enemy, but rather about transforming that data into relevant information in a timely manner for diverse forces with dynamically changing needs. It is a critical component of US military success in multidomain operations, where operations are conducted across land, sea, air, space, and cyberspace.
This is the Army’s high-tech edge. It includes cyber specialists and information warfare experts who protect Army networks, disrupt enemy systems, and manage the flow of digital information to gain the upper hand in both physical and virtual battlespaces.
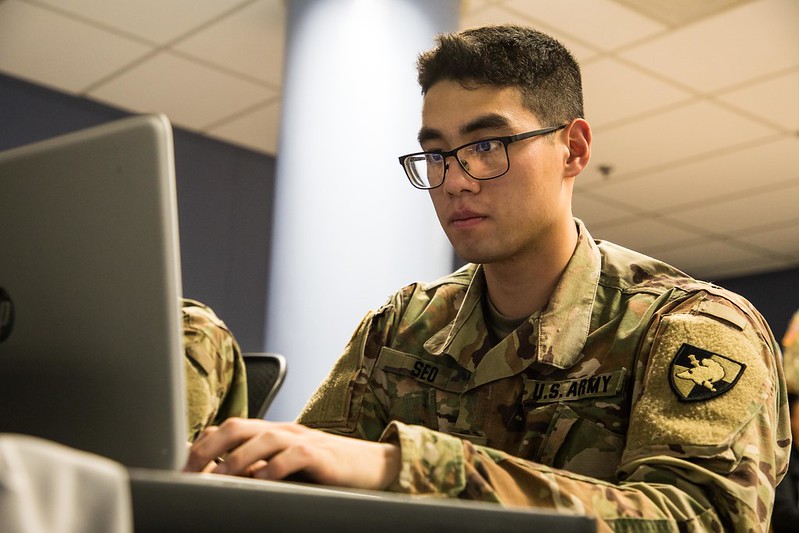

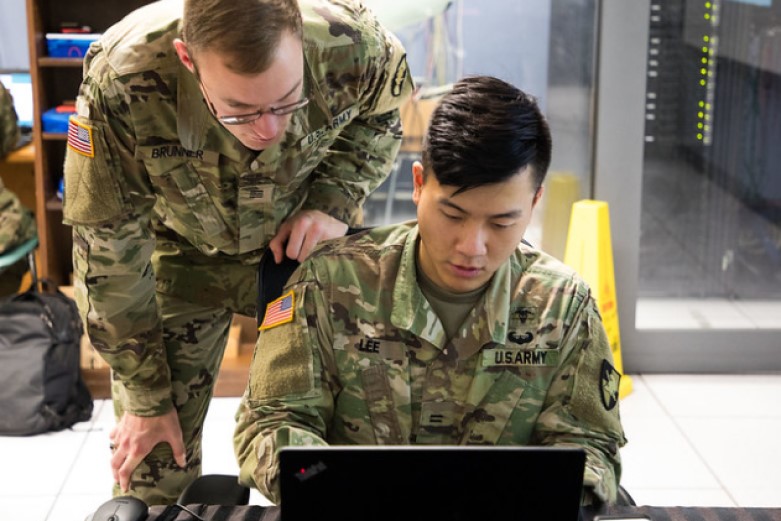
Cyber
Cyber Operations officers conduct integrated and synchronized defensive and offensive cyberspace operations by targeting hostile enemy activities and capabilities.
Virtual Branch Outreach
To enhance the branch education process, the U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command developed Virtual Branch Outreach (VBO). VBO is a public-facing virtual environment designed to provide branching education and assistance to cadets from the United States Military Academy at West Point.
Contact the Accessions Division
The Accessions Division oversees Branch Week, Branch Night, and Post Night, and leads the transition process from cadet to lieutenant during the second semester for the graduating class.
Accessions is a subordinate division of the Department of Military Instruction, comprised of officers who represent the culture and personalities of each of the army branches.

